library(DeclareDesign)
sample_size <- 100
# Declare a two-arm trial in code
two_arm_trial <-
declare_model(N = sample_size,
U = rnorm(N),
potential_outcomes(Y ~ 0.2 * Z + U)) +
declare_inquiry(ATE = mean(Y_Z_1 - Y_Z_0)) +
declare_assignment(Z = complete_ra(N, prob = 0.5)) +
declare_measurement(Y = reveal_outcomes(Y ~ Z)) +
declare_estimator(Y ~ Z, inquiry = "ATE")Declare and diagnose your research design
DeclareDesign is a set of software tools to plan, implement, analyze, and communicate about empirical research
MIDA framework for describing research designs
The MIDA framework describes the four elements of any empirical research design:
- Model: the worlds you consider
- Inquiry: the question you ask
- Data strategy: sampling, treatment assignment, and measurement procedures
- Answer strategy: estimation, testing, interpretation, and visualization procedures
Read Chapter 5 of Research Design in the Social Sciences to learn how these four research design elements connect to reality and simulations that can be used to plan and improve research designs.
Declare-Diagnose-Redesign algorithm for designing research
- Declare designs in code following the MIDA framework.
- Diagnose declared designs through Monte Carlo simulation to learn their properties, such as bias and power.
- Redesign data and answer strategy features to optimize designs under logistical, financial, and ethical constraints.
Here is an illustration of using DeclareDesign for a two-arm randomized trial:
# Draw a simulated dataset
draw_data(two_arm_trial)| ID | U | Y_Z_0 | Y_Z_1 | Z | Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 001 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.71 | 1 | 0.71 |
| 002 | -0.82 | -0.82 | -0.62 | 1 | -0.62 |
| 003 | -0.28 | -0.28 | -0.08 | 1 | -0.08 |
# Obtain a simulated estimate and estimand
run_design(two_arm_trial)| estimate | std.error | p.value | inquiry | estimand |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.18 | 0.2 | 0.37 | ATE | 0.2 |
# Simulate the research design 500 times and
# summarize the simulations
diagnosis <- diagnose_design(two_arm_trial, sims = 500)
tidy(diagnosis)| diagnosand | estimate | std.error |
|---|---|---|
| mean_estimand | 0.200 | 0.000 |
| mean_estimate | 0.198 | 0.009 |
| bias | -0.002 | 0.009 |
| sd_estimate | 0.193 | 0.007 |
| rmse | 0.193 | 0.007 |
| power | 0.148 | 0.015 |
| coverage | 0.954 | 0.010 |
library(ggplot2)
# Visualize simulated sampling distribution
ggplot(data = get_simulations(diagnosis),
aes(x = estimate)) +
geom_histogram() 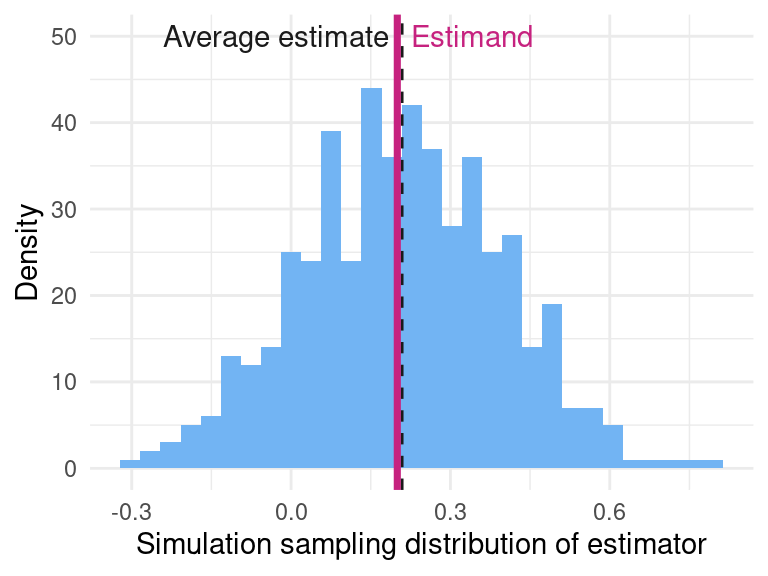
# Redesign over sample size and calculate power
diagnosis <-
two_arm_trial |>
redesign(sample_size = c(250, 500, 750, 1000, 1250)) |>
diagnose_designs() |>
tidy() |>
filter(diagnosand == "power")
# Visualize power curve over sample sizes
ggplot(diagnosis, aes(sample_size, estimate)) +
geom_point() +
geom_line()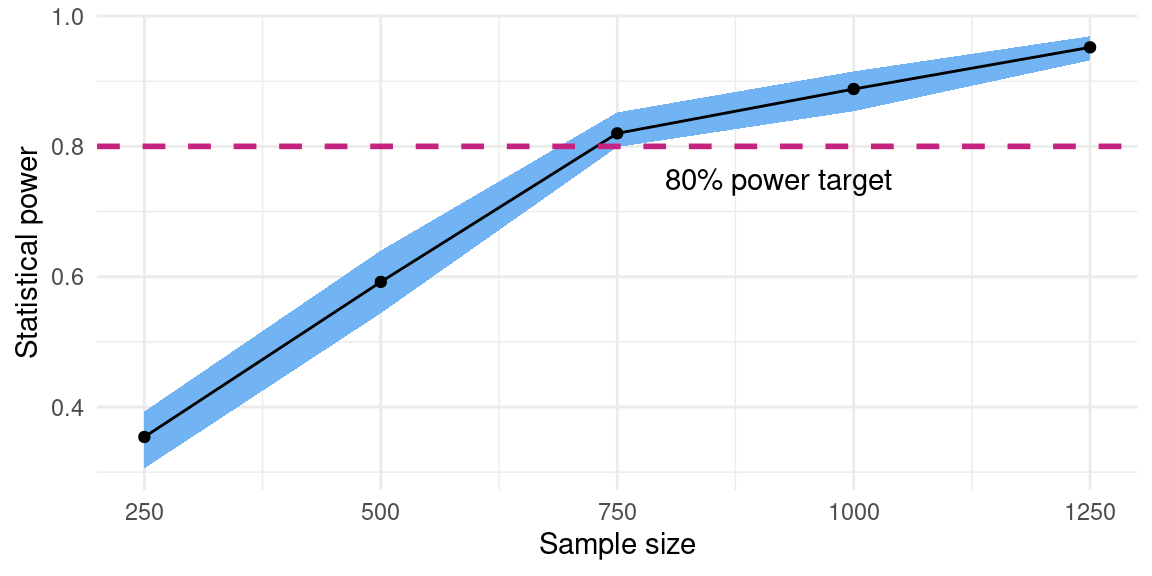
Library of common research designs
The MIDA framework can accomodate observational and experimental, descriptive and causal, qualitative and quantitative research designs. Part III of Research Design in the Social Sciences illustrates the framework for these common designs.
Observational designs for descriptive inference
Simple random sampling
Cluster random sampling
Multi-level regression and poststratification
Index creation
Observational designs for causal inference
Process tracing
Selection-on-observables
Difference-in-differences
Instrumental variables
Regression discontinuity designs
Experimental designs for descriptive inference
Audit experiments
List experiments
Conjoint experiments
Behavioral games
Experimental designs for causal inference
Two-arm randomized experiments
Block-randomized experiments
Cluster-randomized experiments
Subgroup designs
Factorial experiments
Encouragement designs
Placebo-controlled experiments
Stepped-wedge experiments
Randomized saturation experiments
Experiments over networks
Complex designs
Discovery using causal forests
Structural estimation
Meta-analysis
Multi-site studies
